
In the past, infrastructure provisioning was a time-consuming, manual process for all organizations which made it difficult for businesses to keep up with rapidly changing business demands. However, cloud computing has ushered in a new landscape, filled with tools and technologies that can streamline and automate the provisioning process.
We’ll cover what infrastructure provisioning is, why it’s important, and tools organizations can use to provision more effectively as part of their cloud modernization journey.
What is Infrastructure Provisioning?
Infrastructure provisioning, as it pertains to IT, involves the preparation, specification, and activation of IT infrastructure components in a way that enables the availability of necessary computing resources when needed. Such resources can include:
- Servers
- Networks
- Storage
Provisioning is generally done before configuring and deploying resources either locally or in the cloud; and while it may sound like it involves these steps, provisioning is different from configuration and deployment. Provisioning includes the preparatory process needed to get an IT system ready for configuration and can be done in-house or by utilizing Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). During configuration that resources can be allocated, dependencies can be set, and components can be enabled to handle necessary workloads.
Next comes deployment. This is the step when the application or service gets launched and reaches the ultimate end-user. The projects businesses undergo in the provisioning and configuration phases can influence the ease of deployment.
Manual vs. Automated Provisioning
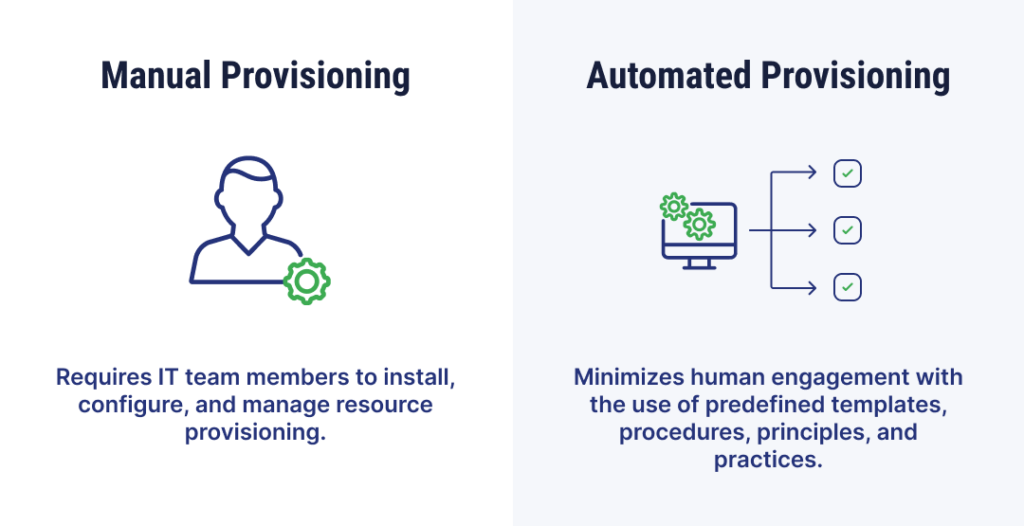
Manual provisioning requires human interaction to install, configure, and manage the provisioning of various resources, such as servers, networks, or applications, typically through repetitive, hands-on tasks carried out by IT personnel. The tasks IT team members may take on also includes installing operating systems and hardware and testing applications. Manual provisioning can be difficult to scale and can also lead to more errors.
Automated provisioning, on the other hand, minimizes the need for human engagement due to the use of predefined templates and procedures. Organizations may implement DevOps principles and practices and use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to define resources, orchestration tools to manage resources, and cloud management tools to manage and provision resources, for example. Automated provisioning can require some upfront setup but can be less error-prone and more efficient than manual provisioning. Additionally, it accelerates the introduction of new IT resources, services, and products to market, enabling IT teams to redirect their focus toward strategic tasks, reducing time spent on repetitive activities.
What Are the Benefits of Automated Infrastructure Provisioning?
Automated provisioning offers several advantages over manual infrastructure provisioning, such as:
- Efficiency: Automated provisioning significantly reduces the time required to set up resources, streamlining processes and enabling quicker deployment.
- Consistency: Automation ensures consistent configurations and setups, minimizing the chances of human error that can often accompany manual processes.
- Productivity: Automated provisioning reduces the need for extensive intervention by team members, which can increase productivity and enable IT teams to focus more time on revenue-generating initiatives or projects to enhance user experience.
- Scalability: With automation, it’s easier to scale operations and deploy resources across various environments efficiently.
- Less Downtime: Automation helps in quick and consistent resource provisioning, reducing downtime and enhancing overall system reliability.
What Are the Different Types of IT Provisioning?
There are several types of infrastructure provisioning, and each addresses specific needs within the IT landscape. Cloud provisioning, network provisioning, server provisioning, account provisioning, and service provisioning can involve both manual and automated processes, however, many aspects of provisioning can be automated at this point.
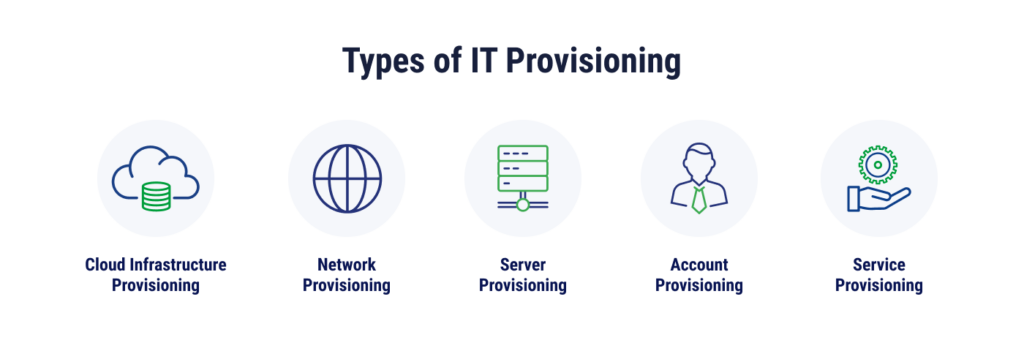
Cloud Infrastructure Provisioning
The goal of cloud infrastructure provisioning is to efficiently establish and manage the resources needed to run applications and services in a cloud environment. With this type of provisioning, organizations can allocate their resources in the cloud to meet their business needs. Computing power, networking, storage, and databases may be provisioned for the cloud.
Network Provisioning
Network provisioning involves the configuration of essential components within an enterprise network, such as routers, switches, firewalls, and access points. It also includes tasks like:
- IP address allocation
- Granting device access to authorized users
- Implementing security measures for network protection
- Setting up access controls
- Ensuring the network is operational and optimized
Server Provisioning
Server provisioning is the process of setting up and configuring various servers, whether they are physical hardware or virtual machines (VMs). It involves the installation and configuration of necessary software, including operating systems (OS), applications, and middleware. Additionally, server provisioning involves defining the intended use of the server, setting it up to meet specific business requirements, and ensuring connectivity to networks and storage systems for operational readiness.
Account Provisioning
Account provisioning (also referred to as user provisioning) is the management of user accounts across various systems and applications used by an organization and involves setting up initial accounts with the correct:
- Credentials
- Access rights
- Permissions
- User roles
Identity management plays a crucial role in this process, encompassing authentication and authorization setups, often utilizing role-based access control (RBAC). When users are provisioned, their access privileges within the network are established, while deprovisioning involves the revocation of these access rights.
User provisioning is key during onboarding and role changes, while deprovisioning is carried out when a user leaves an organization, ensuring that access is granted and revoked accurately to maintain compliance and reduce security risks.
Service Provisioning
Service provisioning refers to the process of setting up and preparing IT services and applications end users may need to complete their daily tasks. Service provisioning commonly includes tasks like configuration, installation, and activation, ensuring that these services are operational and ready for use by authorized users or systems.
With service and application provisioning, IT teams also manage the related data, and monitor the applications and services to discover areas for optimization.
Tools for Infrastructure Provisioning
To make the infrastructure provisioning process more effective, DevOps teams and consultants encourage the use of cloud tools and adoption of IaC.
Well-Architected Frameworks
Businesses looking to create reliable, scalable, high-quality IT systems may look to well-architected frameworks for guidance. Cloud providers have created these frameworks to outline best practices for organizations looking to develop and deploy complex IT systems in the cloud. While each provider has slightly different principles outlined, all frameworks focus on security, efficiency, reliability, cost optimization, and scalability.
Examples of well-architected frameworks include:
- AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Google Cloud Architecture Framework
- Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework
- OpenStack Architecture Design Guide
Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code is just like how it sounds – infrastructure is defined and managed using code instead of infrastructure resources being manually configured. Tools that might be used alongside IaC for infrastructure provisioning are Azure Resource Manager, Pulumi, AWS CloudFormation, and Google Cloud Deployment Manager.
Other Ideas
Some other tools that may come in handy for infrastructure provisioning are as follows:
- Cloud Management Tools: AWS Management Console, Google Cloud Console, and Azure Portal
- Infrastructure Monitoring Tools: Nagios Core, Prometheus, and DataDog
- Orchestration Tools: Docker Swarm and Kubernetes
- Infrastructure Configuration Tools: Red Hat Ansible and Puppet
Build the Right Cloud Infrastructure Provisioning Strategy
Starting with a solid foundation is the most surefire way to ensure the deployment of your applications and services runs smoothly. This isn’t possible without a solid cloud infrastructure procurement strategy in place. If you’re trying to figure out where to start, TierPoint can help. Our cloud experts can assist you in building the strategy that ladders up to a seamless launch..
Do you have the talent in-house to successfully handle your infrastructure provisioning as you unlock efficiency during a cloud migration? Download our eBook to discover the skills you should have on your team to ensure everything runs smoothly.

